10 May 2023
Controlling the customer relationship by selling direct
Direct distribution is a marketing strategy wherein goods or services are sold DIRECTLY from the manufacturer or producer to the end consumer without involving intermediaries such as distributors, retailers, wholesalers, agents, or stockists.
An example would be a steel fabrication business that receives orders from a builder to fabricate a steel structure required for a construction project. The steel fabricator is dealing direct with the customer, and delivers direct to the customer's construction site. They then invoice the customer direct. In direct distribution the manufacturer knows who the customer is and if desired can maintain a business relationship with that customer to generate future sales.
By contrast, when using an IN-DIRECT distribution model the manufacturer first sells their product to an intermediary such as wholesalers, retailers, or agents. Typically they may not know who the end-user is.
Deciding to sell DIRECT or to sell via intermediaries (DISTRIBUTORS) which is termed INDIRECT distribution, is a strategic marketing decision made by companies as part of their marketing strategy.
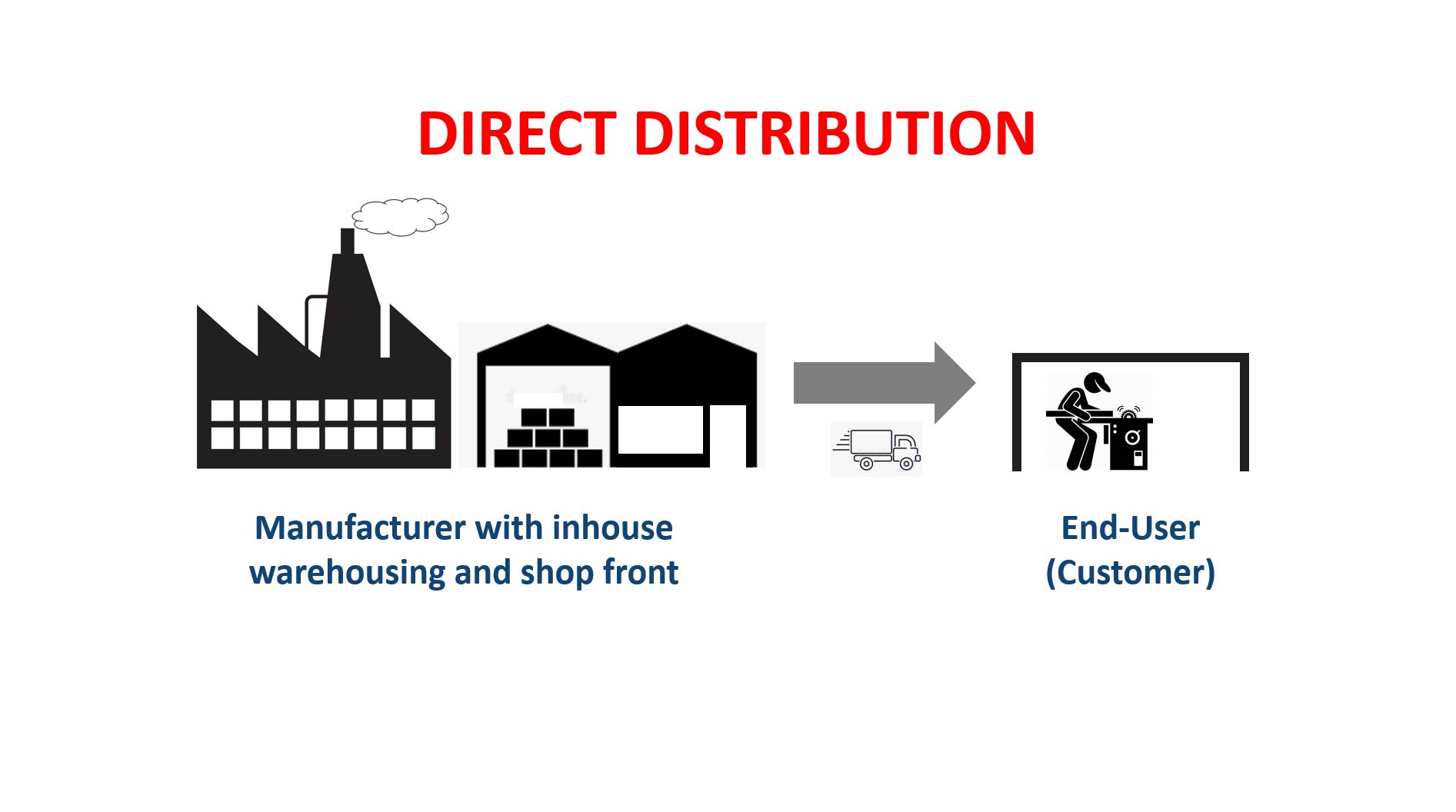
Direct distribution: the manufacturer (or important distributor) sells direct to their customer.
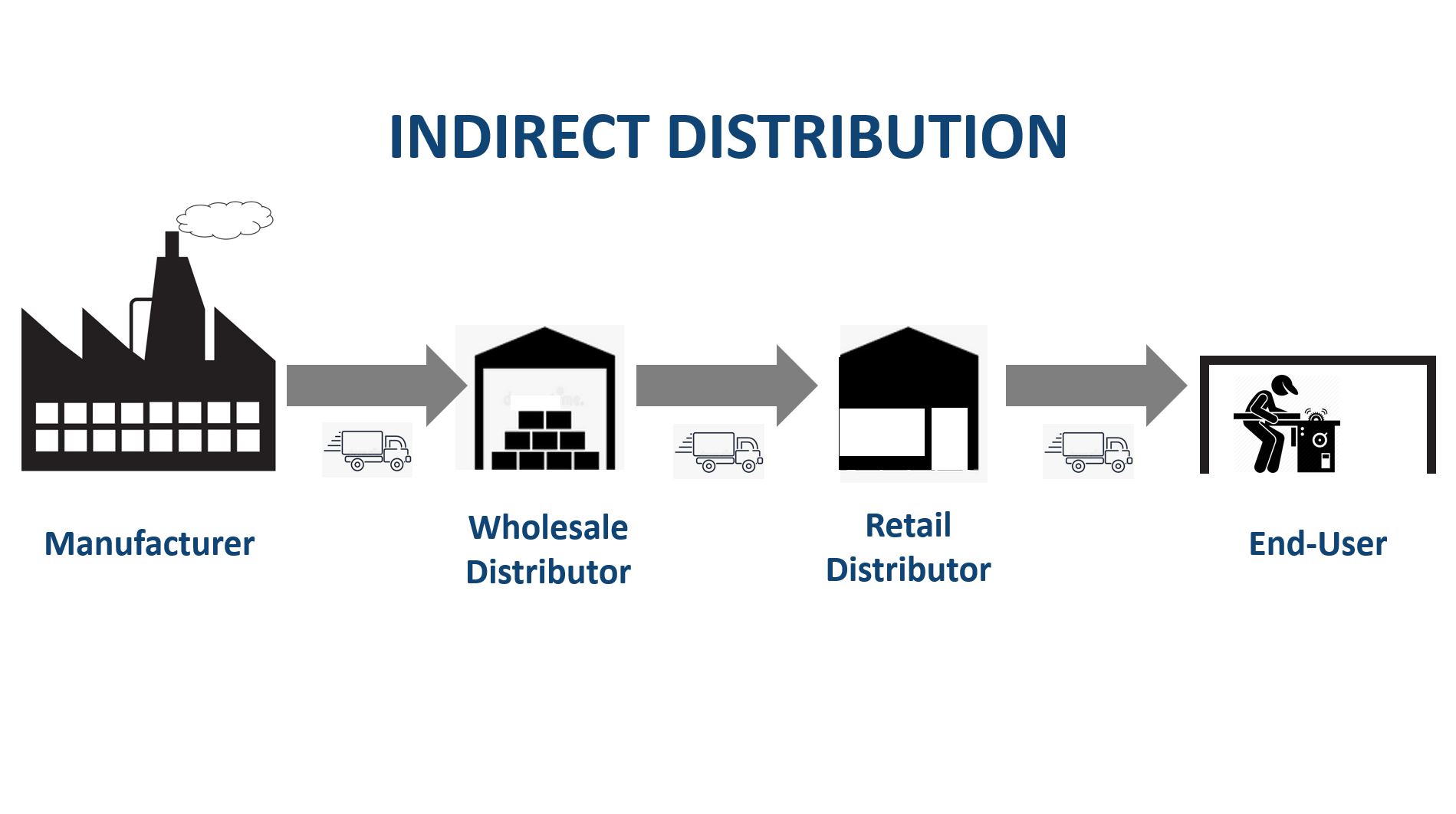
Indirect distribution: alternatively, the organization sells first to intermediaries (distributors). Distributors then sell to the end-users (buyers). It is apparent that the originator of the product is less able to develop and maintain a relationship with the end-user when selling via distributors.
Key Components of Direct Distribution
-
Manufacturer-to-Consumer Relationship: Direct distribution involves establishing a direct relationship between the manufacturer or producer and the end consumer. The company takes on the responsibility of marketing, selling, and delivering its products or services directly to customers.
-
Online Platforms and E-commerce: With the rise of e-commerce and online platforms, direct distribution has become more accessible and feasible for businesses. Companies can leverage their websites, online marketplaces, or mobile apps to showcase and sell their products directly to customers, regardless of geographical limitations.
-
Control over the Entire Sales Process: In direct distribution, the company has complete control over the sales process, including pricing, promotions, product positioning, and customer service. This control allows for greater flexibility and agility in adapting to market changes and customer preferences.
Direct distribution isn't appropriate for all businesses
Before we delve into the advantages and disadvantages of DIRECT DISTRIBUTION it needs to be noted that for many businesses indirect distribution is simply not possible or not worth the trouble. Businesses that sell customised product (engineering fabrication for example, or professional services such as accounting, solicitors, consulting engineers, project managers etc.) cannot be sold indirect (via a distributor).
Indirect distribution is more suited to volume products of fixed specification.
Advantages of Direct Distribution
-
Increased Profitability: Direct distribution eliminates the costs associated with intermediaries, such as wholesale margins, retailer markups, or commissions. As a result, companies can retain a higher percentage of the sales revenue, leading to increased profitability.
-
Greater Customer Insights: By interacting directly with customers, companies gain valuable insights into customer preferences, behavior, and feedback. This enables them to tailor their offerings, marketing messages, and customer experiences to meet specific needs, fostering customer loyalty and satisfaction.
-
Enhanced Brand Control: Direct distribution empowers companies to maintain consistent brand messaging, positioning, and image throughout the entire customer journey. Without intermediaries, the company has full control over how its products are presented and perceived by customers.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: Direct distribution allows companies to respond quickly to market trends, launch new products or services, and adjust pricing or promotional strategies in a timely manner. This flexibility enhances competitiveness and agility in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
-
Direct Customer Relationships: Building direct relationships with customers fosters trust, loyalty, and long-term engagement. It enables companies to gather customer data, personalize marketing efforts, and provide exceptional customer service, leading to higher customer retention rates and repeat business.
-
Avoiding the complexity of managing marketing channels: Managing distributor relationships requires dedicated resources to nurture distributor relationships, provide training, supply promotional materials, coordinate product deliveries, problem solving, and often negotiating volume pricing when the distributor is trying to close a large sale.
Disadvantages of direct distribution
Direct distribution is usually not the best distribution strategy for high volume product sales such as FMCG where an intensive distribution strategy would make the manufacturer's products more easily accessible to consumers thus maximizing exposure to the largest possible number of potential customers.
Best Practices for Direct Distribution
-
Strong Online Presence: Establish a robust online presence through a user-friendly website, engaging content, and optimized e-commerce platforms. Leverage social media, search engine optimization (SEO), and online advertising to drive traffic and conversions.
-
Seamless Purchasing Experience: Focus on providing a seamless and convenient purchasing experience for customers. Optimize website navigation, offer secure payment options, and ensure prompt order fulfillment and delivery.
-
Customer Relationship Management: Implement effective customer relationship management (CRM) systems to track customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history. Leverage this data to personalize marketing messages, offers, and recommendations.
-
Effective Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Direct distribution requires efficient logistics and supply chain management. Streamline inventory management, warehousing, and order fulfillment processes to ensure timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regularly analyze customer feedback, sales data, and market trends to identify areas for improvement. Adapt strategies, refine offerings, and innovate based on customer needs and changing market dynamics.
Company-owned Retail Stores
One of the principle disadvantages of direct distribution is not having products stocked close to all geographic markets. In Australia for example, a manufacturer (or import distributor) may be located in (say) Melbourne but have national market opportunities. Selling direct would imply one sales outlet being the company owned premises in Melbourne.
To improve geographic market coverage the company will need to establish a physical presence in other states potentially in capital cities and major regional towns. The choices are to either appoint distributors (indirect distribution) or set-up company owned retail outlets.
For businesses with physical products, establishing company-owned retail stores provides a direct link between the manufacturer and the consumer. This method offers complete control over the shopping experience, allowing businesses to create brand awareness, engage with customers, and gather valuable feedback. Company-owned retail stores enable businesses to showcase their entire product range, provide exceptional customer service, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Having company owned retail outlets provides greater opportunity to maximize a place strategy where the aim is to control the place where customers come to consider, purchase,and obtain after sales service.
However, the cost for doing so needs to be weighed-up against the likely return on investment (both initial capital and ongoing operational costs).
If intensive distribution is better suited to the product and industry category then company owned retail outlets is likely to be a flawed strategy.
However, if it is sufficient to have a single store in each capital city then company owned and operated outlets may be the preferred option.
Conclusion
Direct distribution offers companies numerous advantages by establishing a direct link between the manufacturer and the end consumer. It enables businesses to control the entire sales process, build direct customer relationships, and maximize profitability. However, the choice between direct and indirect distribution ultimately depends on various factors such as the nature of the product, target market, resources available, and geography.
Direct distribution is often a preferable distribution strategy for fledgling firms during their start-up phase where they can maximize profitability while establishing a local market before market expansion.
Further reading
The Place Strategy in marketing
Distribution strategy
What is marketing?
What is a selling model?
